Windows Vista introduces a number of new features to the TCP/IP stack, including CTCP, and TCP Window Auto-Tuning. This new implementation works much better by default than previous Windows versions with broadband internet connections, and is able to adjust the RWIN value on the fly, depending on the BDP (bandwidth-delay product). This, however, introduces some problems with older routers and restricts the user from tweaking some of the TCP/IP parameters. Still, there is always some room for improvement, and this article explains the known tweakable TCP/IP parameters.
To enter some of the commands below, you will need to run "elevated" command prompt. To do so, click the Start icon > Run > type: cmd , then click CTRL+SHIFT+ENTER. Alternatively, you can navigate to Start > All Programs > Accessories > right-click Command Prompt and choose "Run as Administrator".
Check the TCP/IP state
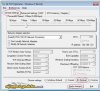
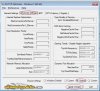
To check the current status of the Vista TCP/IP tweakable parameters, in elevated command prompt type the following command:
netsh int tcp show global
You will be presented with something like the following:
The settings, as well as their default and recommended state are explained below. The two most important tweakable parameters are "Auto-Tuning Level" and "Congestion Control Provider".
When checking the TCP state with the "netsh int tcp show global" command, it is also possible to see the following message below all those parameters:
** The above autotuninglevel setting is the result of Windows Scaling heuristics overriding any local/policy configuration on at least one profile.
It is displayed when the "Receive Window Auto-Tuning Level" is not explicitly set, or if the system deemed it necessary to make a change because of user prompted "repairing" of your network connection, for example.
Disable Windows Scaling heuristics
Windows Vista/7 has the ability to automatically change its own TCP Window auto-tuning behavior to a more conservative state regardless of any user settings. It is possible for Windows to override the autotuninlevel even after an user sets their custom TCP auto-tuning level. When that behavior occurs, the "netsh int tcp show global" command displays the following message:
** The above autotuninglevel setting is the result of Windows Scaling heuristics
overriding any local/policy configuration on at least one profile.
To prevent that behavior and enforce any user-set TCP Window auto-tunning level, you should execute the following command:
netsh int tcp set heuristics disabled
possible settings are: disabled,enabled,default (sets to the Windows default state)
recommended: disabled (to retain user-set auto-tuning level)
Note this should be executed in elevated command prompt (with admin priviledges) before setting the autotuninlevel in next section. If the command is accepted by the OS you will see an "Ok." on a new line.
The corresponding Registry value (not necessary to edit if setting via netsh) is located in:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\services\Tcpip\Parameters
EnableWsd=0 (default: 1, recommended: 0)
TCP Auto-Tuning
To turn off the default RWIN auto tuning behavior, (in elevated command prompt) type:
netsh int tcp set global autotuninglevel=disabled
The default auto-tuning level is "normal", and the possible settings for the above command are:
disabled: uses a fixed value for the tcp receive window. Limits it to 64KB (limited at 65535).
highlyrestricted: allows the receive window to grow beyond its default value, very conservatively
restricted: somewhat restricted growth of the tcp receive window beyond its default value
normal: default value, allows the receive window to grow to accommodate most conditions
experimental: allows the receive window to grow to accommodate extreme scenarios (not recommended, it can degrade performance in common scenarios, only intended for research purposes. It enables RWIN values of over 16 MB)
Our recommendation: normal (unless you're experiencing problems).
If you're experiencing problems with your NAT router or SPI firewall, try the "restricted", "highlyrestricted", or even "disabled" state.
Notes:
- Reportedly, some older residential NAT routers with a SPI firewall may have problems with enabled tcp auto-tuning in it's "normal" state, resulting in slow speeds, packet loss, reduced network performance in general.
- auto-tuning also causes problems with really old routers that do not support TCP Windows scaling. See MSKB 935400
- netsh set commands take effect immediately after executing, there is no need to reboot.
- sometimes when using "normal" mode and long lasting connections (p2p software / torrents), tcp windows can get very large and consume too much resources, if you're experiencing problems try a more conservative (restricted) setting.
If you're experiencing problems with Auto-Tuning, see also:
MS KB 835400 - email issues
MS KB 934430 - network connectivity behind firewall problems
MS KB 940646 - 3G WWAN throughput issues
MS KB 929868 - web browsing issues
MS KB 932170 - slow network file transfer
Compound TCP - Improve throughput
Add-On Congestion Control Provider
The traditional slow-start and congestion avoidance algorithms in TCP help avoid network congestion by gradually increasing the TCP window at the beginning of transfers until the TCP Receive Window boundary is reached, or packet loss occurs. For broadband internet connections that combine high TCP Window with higher latency (high BDP), these algorithms do not increase the TCP windows fast enough to fully utilize the bandwidth of the connection.
Compound TCP (CTCP) is a newer method, available in Vista and Server 2008 (there is also a hotfix available for XP/2003). CTCP increases the TCP send window more aggressively for broadband connections (with large RWIN and BDP). CTCP attempts to maximize throughput by monitoring delay variations and packet loss. It also ensures that its behavior does not impact other TCP connections negatively.
By default, Vista and Windows 7 have CTCP turned off, it is only on by default under Server 2008. Turning this option on can significantly increase throughput.
To enable CTCP, in elevated command prompt type:
netsh int tcp set global congestionprovider=ctcp
To disable CTCP:
netsh int tcp set global congestionprovider=none
Possible options are: ctcp, none, default (restores the system default value).
Recommended setting: ctcp
It is better to use this newer generation CTCP congestion control algorithm for most broadband connections, we highly recommend it being turned on.
ECN Capability
ECN (Explicit Congestion Notification, RFC 3168) is a mechanism that provides routers with an alternate method of communicating network congestion. It is aimed to decrease retransmissions. In essence, ECN assumes that the cause of any packet loss is router congestion. It allows routers experiencing congestion to mark packets and allow clients to automatically lower their transfer rate to prevent further packet loss. Traditionally, TCP/IP networks signal congestion by dropping packets. When ECN is successfully negotiated, an ECN-aware router may set a bit in the IP header (in the DiffServ field) instead of dropping a packet in order to signal congestion. The receiver echoes the congestion indication to the sender, which must react as though a packet drop were detected.
ECN is disabled by default in Vista and other modern TCP/IP implementations, as it is possible that it may cause problems with some outdated routers that drop packets with the ECN bit set, rather than ignoring the bit. To check whether your router supports ECN, you can use the Microsoft
Internet Connectivity Evaluation Tool. The results will be displayed under "Traffic Congestion Test".
To enable ECN, in elevated command prompt type:
netsh int tcp set global ecncapability=enabled
Possible settings are: enabled, disabled, default (restores the state to the system default).
The default state is: disabled
Recommendation: enabled (only for short-lived, interactive connections and HTTP requests with routers that support it, in the presense of congestion/packet loss), disabled otherwise (for pure bulk throughput with large TCP Window, no regular congestion/packet loss, or outdated routers without ECN support).
Notes: ECN is only effective in combination with AQM (Active Queue Management) router policy. It has more noticeable effect on performance with interactive connections and HTTP requests, in the presense of router congestion/packet loss. Its effect on bulk throughput with large TCP Window are less clear.
More information on ECN:
Explicit Congestion Notification (ECN) for TCP/IP
RSS - Receive-side Scaling
The receive-side scaling setting enables parallelized processing of received packets on multiple processors, while avoiding packet reordering. It avoids packet reordering y separating packets into "flows", and using a single processor for processing all the packets for a given flow. Packets are separated into flows by computing a hash value based on specific fields in each packet, and the resulting hash values are used to select a processor for processing the flow. This approach ensures that all packets belonging to a given TCP connection will be queued to the same processor, in the same order that they were received by the network adapter.
To set RSS:
netsh int tcp set global rss=enabled
Possible rss settings are: disabled, enabled, default (restores rss state to the system default).
Default state is: enabled
Recommended: enabled (if you have 2 or more processor cores and a NIC that can handle RSS)
TCP Chimney Offload
TCP chimney offload enables Windows to offload all TCP processing for a connection to a network adapter. Offloads are initiated on a per-connection basis. Compared to task offload, TCP chimney offload further reduces networking-related CPU overhead, enabling better overall system performance by freeing up CPU time for other tasks.
To set TCP Chimney Offload:
netsh int tcp set global chimney=enabled
Default state: disabled (under Vista), automatic (under Windows 7 and 2008 Server)
Recommended: enabled
The possible states are disabled, enabled, default (Vista), automatic (only Windows 7 and 2008 Server) as follows:
automatic - This default setting is only available under Windows 7 and 2008 Server, it is not available udner Vista. It offloads if the connection is 10 GbE, has a RTT < 20ms, and the connection has exchanged at least 130KB of data. The device driver must also have TCP Chimney enabled.
default - this setting restores chimney offload to the system default. Setting this "default" state under Windows 7 and 2008 Server is possible, but it sets the system to the "automatic" mode described above.
disabled - this setting is maually configured as disabled.
enabled - this setting is manually configured as enabled.
Notes:
Under Windows 7 and Server 2008 the "default" and the additional "automatic" parameter set the system to the same "automatic" state.
For Chimney Offload to work, it needs to be enabled in both the OS and NIC. To enable the "TCP Offloading" setting in your NIC, navigate to the Device Manager, under Network Adapters, in the Advanced tab, and check "Enabled" in the box next to the TCP offload entry.
Direct Cache Access (DCA)
Windows 7 and 2008 Server (but not Vista) add NETDMA 2.0 Direct cache access support. Direct Cache Access (DCA) allows a capable I/O device, such as a network controller, to deliver data directly into a CPU cache. The objective of DCA is to reduce memory latency and the memory bandwidth requirement in high bandwidth (Gigabit) environments. DCA requires support from the I/O device, system chipset, and CPUs.
To enable DCA:
netsh int tcp set global dca=enabled
Available states are: enabled, disabled.
Default state: disabled
Recommended: enabled (provided the CPU/Chipset/NIC support it)
It is also possible to enable this setting by editing the Windows Registry instead of using netsh as follow